-Xms4g
Configuration File Locations¶
Most installations of Elasticsearch have the default configuration location at /etc/elasticsearch/.
The default location depends on whether the installation is from an archive distribution (.tar.gz or .zip file) or a package distribution (Debian or RPM packages). For more info on Elasticsearch configuration, please read Configuring Elasticsearch.
All commands on this page assume Elasticsearch was installed via a Debian or RPM package.
Other Default Locations¶
Depending on the installation method the default location for Elasticsearch configuration and binary files can change. Use these Elasticsearch docs for more information:
Configure Elasticsearch¶
Increase Bulk Queue Size¶
Increase the bulk queue size of Elasticsearch by running the following command:
echo 'thread_pool.write.queue_size: 2000' \
| sudo tee --append /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Increase Heap Size¶
Increase the default heap size of elasticsearch by editing /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options.
Set Xmx and Xms to no more than 50% of the machine's physical RAM.
Elasticsearch requires memory for purposes other than the JVM heap and it is important to leave available memory (RAM) space for this.
Example¶
If you have 16 GB of physical RAM, change the settings from:
$ sudo grep 'Xm' /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options
# -Xms4g
# -Xmx4g
to:
$ sudo grep 'Xm' /etc/elasticsearch/jvm.options
-Xms8g
-Xmx8g
In the above example, we set the minimum and maximum heap size to 8 GB.
Increase Log Compression¶
Set the following index codec by running the following command:
echo 'index.codec: best_compression' \
| sudo tee --append /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Increase Number of Available Memory Maps¶
Elasticsearch uses an mmapfs directory by default to store its indices.
The default operating system limits on mmap counts is likely to be too low, which may result in out of memory exceptions.
To increase the limits, run the following command:
sudo sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
To make this change persist across reboots run this command:
echo "vm.max_map_count = 262144" \
| sudo tee --append /etc/sysctl.d/10-elasticsearch.conf
Increase Number of File Descriptors¶
Note: This section is only required for non-package installations. Debian and RPM packages already use the intended value.
Elasticsearch needs max file descriptors system settings to be at least 65536,
which can be updated with this command:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/security/limits.conf.d
echo 'elasticsearch - nofile 65536' \
| sudo tee --append /etc/security/limits.conf.d/elastic.conf
Enable Security Features¶
Enable the Elasticsearch security features to enable basic authentication. Basic authentication is available as part of the basic Elasticsearch license, but disabled by default.
Run the following command to allow access to the cluster using username and password authentication:
echo 'xpack.security.enabled: true' \
| sudo tee --append /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
Start Elasticsearch¶
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch.service
After a short period of time, it is possible to verify that the Elasticsearch node is running by sending an HTTP request to port 9200 on localhost:
curl "localhost:9200"
Securing Elasticsearch¶
Set Passwords for Default User¶
In the Elasticsearch home folder run one of the following commands to setup the default passwords for the built-in elastic user.
This commands creates a random secure password:
echo y | /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords auto
This commands sets a self-assigned password:
/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive
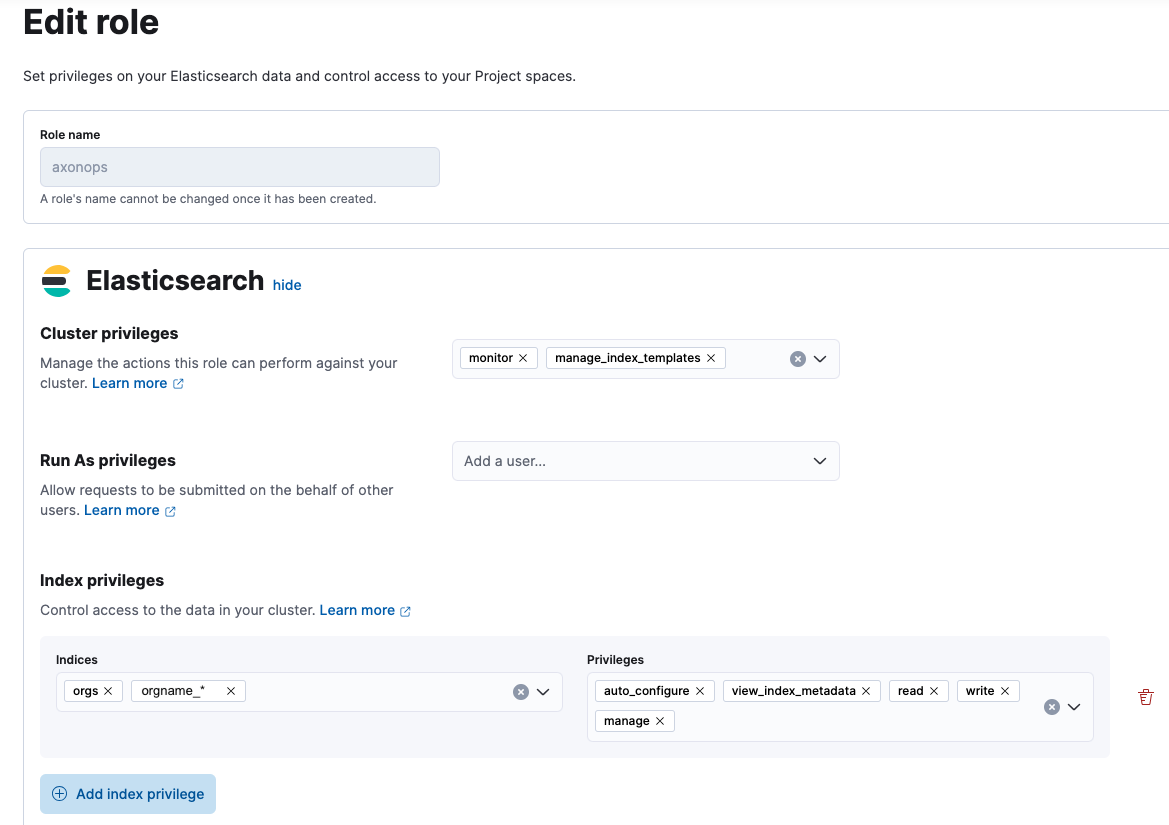
Create a Dedicated Role¶
When creating a dedicated AxonOps role in Elasticsearch, the following privileges are required:
- Cluster privileges:
monitormanage_index_templates
- Index privileges:
auto_configuremanagereadview_index_metadatawrite
The index privileges should be applied to the the following indices:
orgsorgname_*- Where the
orgnameprefix should match theorg_namevalue in the AxonOps server and agent config files.
- Where the
Advanced User Setups¶
You can learn more about other User Authentication options using the Elastic's official documentation.