Kafka Brokers¶
What is a Broker¶
A Kafka broker is a server that stores data and handles all data streaming requests in an Apache Kafka cluster. Each running instance of the Kafka server process is called a broker. Brokers manage the storage of messages in topics, handle read and write requests from clients (producers and consumers), and ensure data is distributed and replicated for scalability and reliability.
-
Cluster Formation: Multiple brokers form a Kafka cluster. Each broker is identified by a unique numeric ID. The cluster distributes topic partitions across brokers, allowing Kafka to scale horizontally and handle high throughput.
-
Data Management: When producers send messages, they are written to specific partitions on brokers. Consumers fetch data directly from the broker storing the partition.
-
Metadata Coordination: Historically, Kafka used ZooKeeper to coordinate brokers and manage metadata, but since Kafka 4.0, this has shifted to KRaft, Kafka’s built-in Raft-based metadata management system.
-
Physical Deployment: Brokers can run on physical servers, cloud instances, or even small devices like Raspberry Pi.
Broker Configuration¶
Broker configuration consists of settings that control how each broker operates within the Kafka cluster.
These configurations are typically defined in a properties file (like server.properties) and can be customized per broker.
Note
Some parameters are specific to KRaft mode or ZooKeeper mode. KRaft is the default for new clusters as of recent Kafka versions
Example Broker Configuration Snippet¶
broker.id=0
log.dirs=/var/lib/kafka/data
num.partitions=4
default.replication.factor=2
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://my-broker.example.com:9092
zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181
auto.create.topics.enable=true
log.retention.hours=168
Networking and Listeners¶
-
listeners: Defines the network interfaces and ports the broker will listen on for client connections.
-
advertised.listeners: Specifies the addresses clients should use to connect, which can differ from internal addresses (useful for NAT, proxies, or external DNS).
-
inter.broker.listener.name: When multiple listeners are configured, this property specifies which one brokers should use for inter-broker communication.
Operational Notes¶
Each broker in a cluster must have a unique broker.id.
Configuration can be fine-tuned for performance, fault tolerance, and network setup.
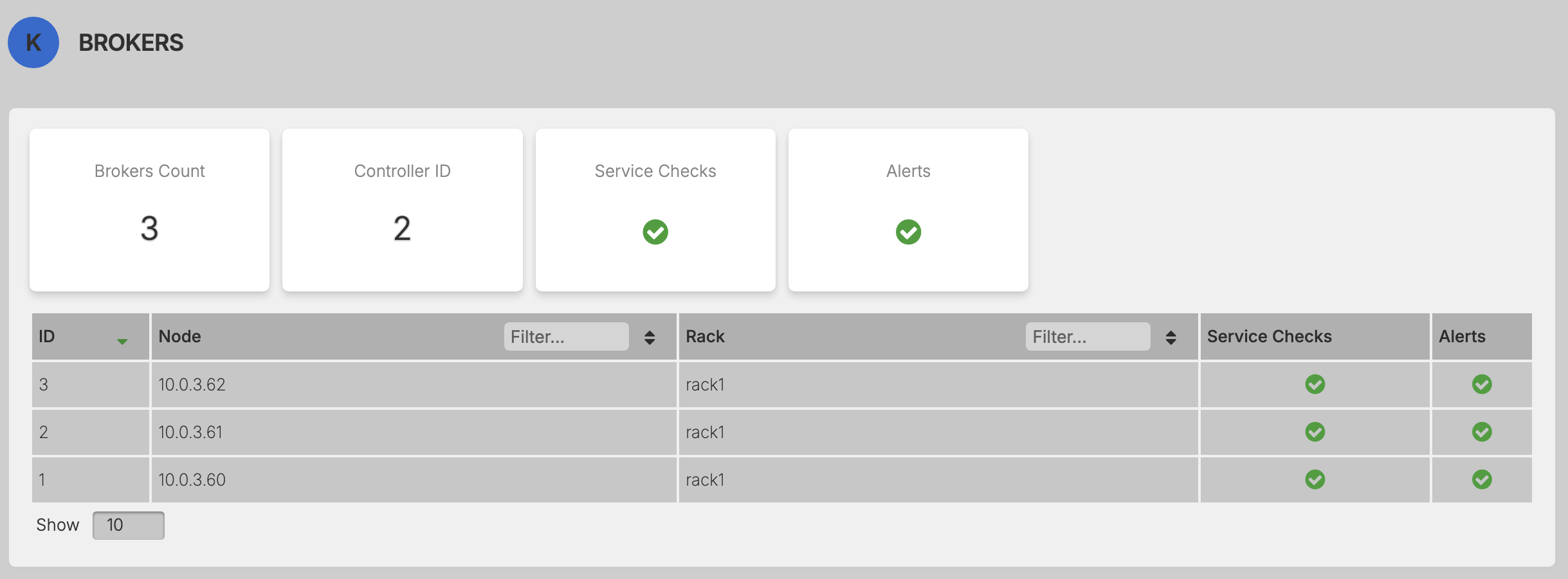
View Broker List,Broker Metrics and Broker Configuration¶
Click Brokers in the Left Navigation¶
Navigate to the Brokers section.
Click on any of the Brokers in the list.¶
Select a specific broker and access detailed broker information.
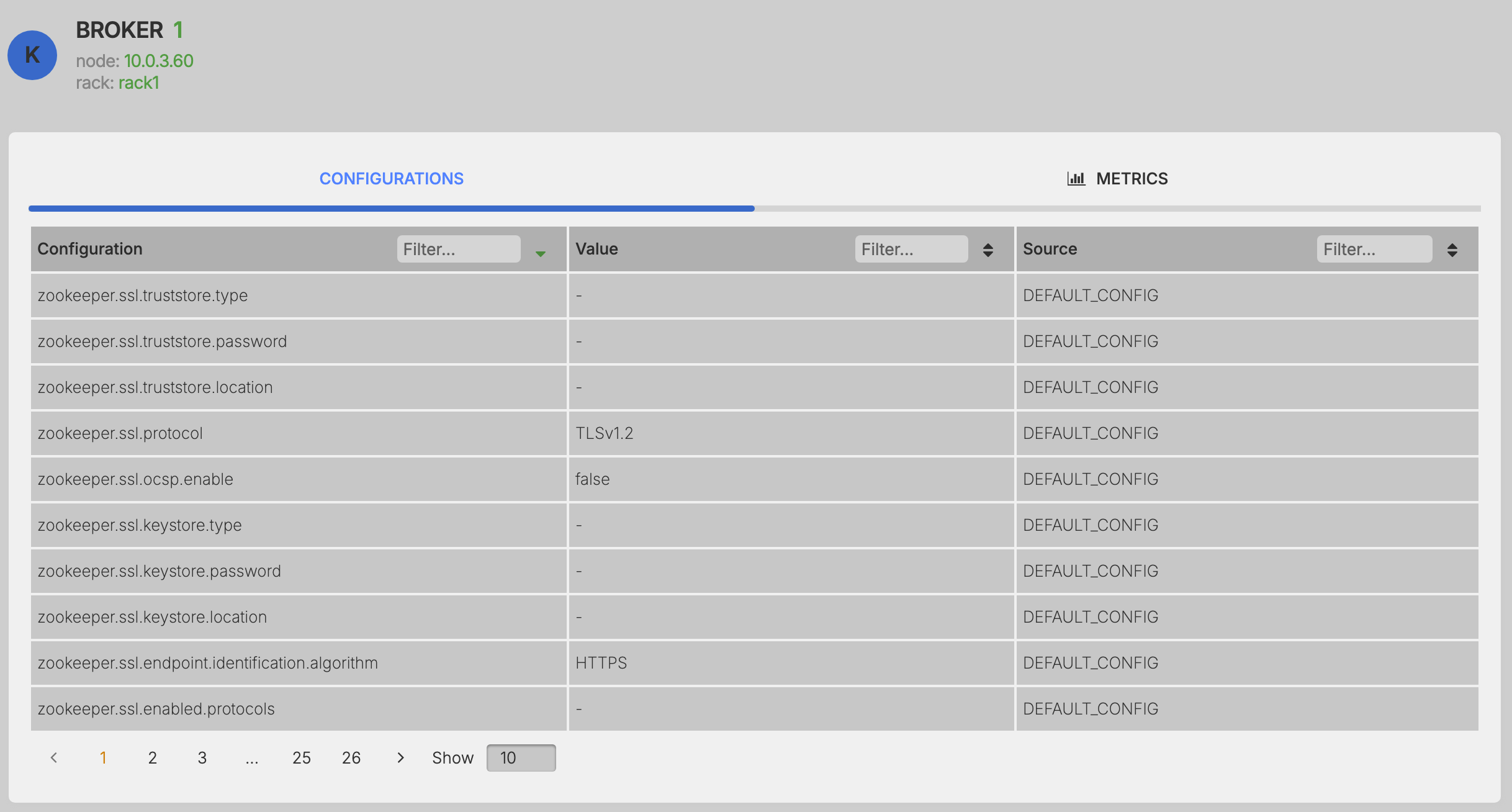
Configurations¶
Access and view all the configurations settings. This cannot be changed or updated from the UI and needs to be updated on the Broker configuration file.
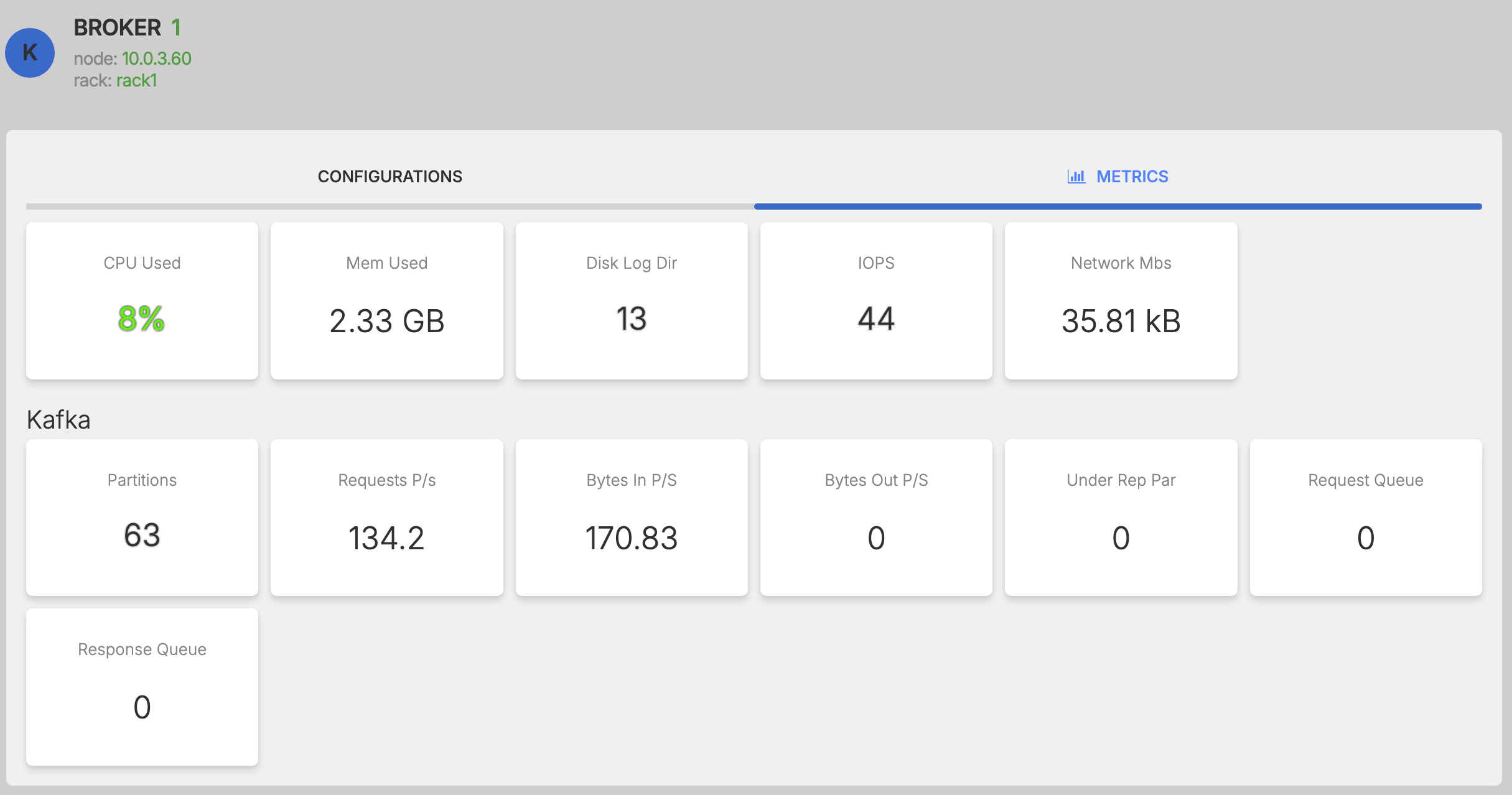
Metrics¶
View performance metrics for the specific Broker.